Radiotherapy Department
1. Radiation Therapy Consultant: Conducts a medical examination of the patient, reviews the patient's records, determines whether the patient requires radiation, designs and outlines the treatment plan, specifies the number of sessions needed, selects the treatment technique to be used, explains the treatment plan to the patient including potential side effects during and after treatment, and oversees regular follow-ups during and after the treatment period. The consultant also directly supervises the implementation of the treatment plan and monitors the patient's progress throughout and after the treatment sessions.
2. Radiation Therapy Specialist: Assists the consultant by directly overseeing the implementation of each patient's treatment plan, from radiation planning to the completion of sessions. The specialist reviews all patient records, ensures that the treatment plan is followed as approved by the consultant, supervises each session, monitors daily imaging during sessions, handles daily patient follow-ups in case of complications, and writes medical reports immediately after the patient completes the sessions.
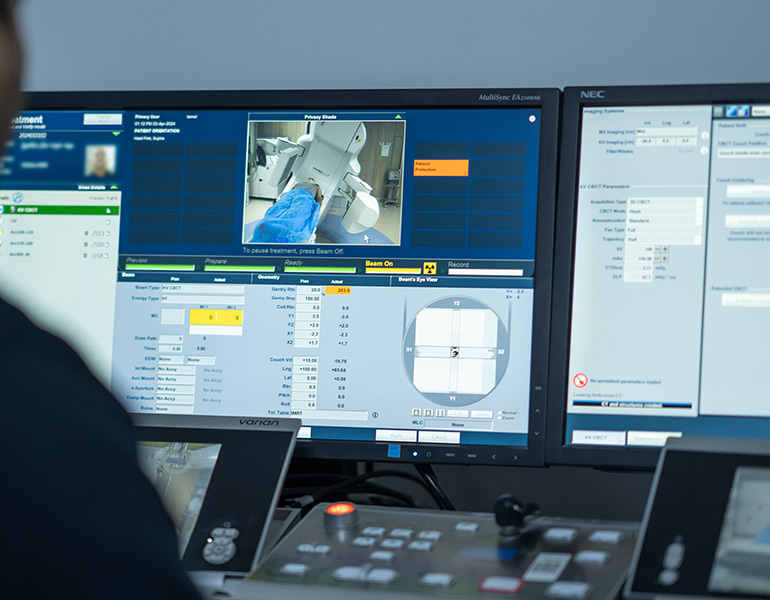
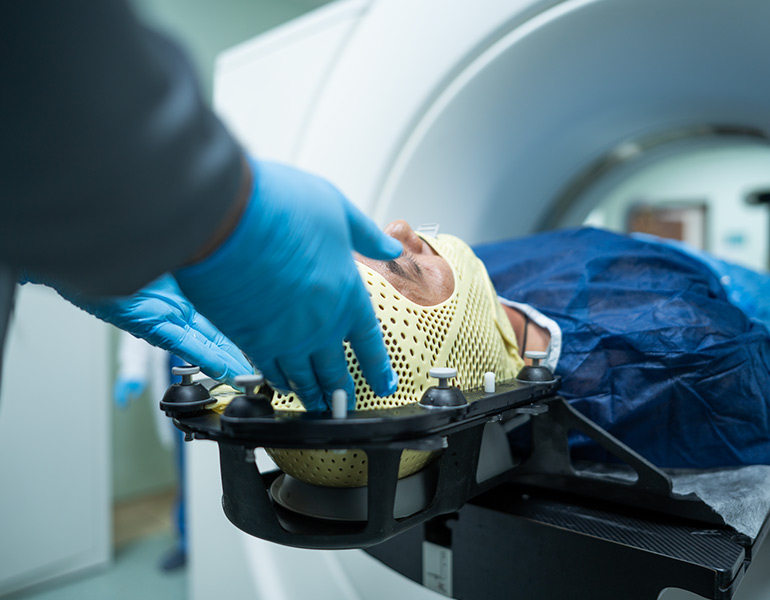
3. Radiation Therapy Department: Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that uses concentrated energy beams to destroy cancer cells. It often employs X-rays, but other forms of radiation therapy, such as proton therapy, are also used. Radiation therapy works by damaging the genetic material that controls cell growth and division. While healthy cells can also be affected, they can repair themselves more easily than cancer cells. The goal of radiation therapy is to treat cancer while minimizing damage to as few healthy cells as possible.
4. Types of Radiation Therapy:
1- Brachytherapy: Also known as internal radiation therapy, this treatment involves placing a small, solid radioactive implant directly into or near the cancer site.
2- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT): This is the most common type of radiation therapy, using a large machine called a linear accelerator to deliver high-energy beams to precise locations in the body.
Available Techniques:
1- Three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy: A type of radiation therapy that uses high-energy beams to kill cancer cells. In Three-dimensional conformal treatment, the beams are carefully shaped to match the tumor shape.
2- Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT): It is an advanced type of radiation therapy. IMRT precisely tailors radiation beams to conform to the shape of the tumor, delivering the appropriate dose of radiation with maximum safety and effectiveness. This method is used to treat tumors in areas such as the head and neck, prostate, pelvis, and lungs.
3- Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT): This method delivers radiation continuously while the machine rotates around the patient, allowing for precise beam shaping to match the tumor’s shape and minimizing the dose to surrounding healthy tissues. It is used to treat various tumors in different locations, often combined with image-guided radiation therapy to enhance accuracy. VMAT typically takes less time than intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT).
4- Image-guided radiation Therapy (IGRT): A type of radiation therapy that uses imaging techniques during each treatment session to enhance accuracy and precision.
5- Rapid Arc Radiation Therapy: A technique that provides a fast and precise form of image-guided, intensity-modulated radiation therapy. It closely conforms to the three-dimensional shape of the tumor.
6- Surface-guided Guided Radiation Therapy (SGRT): It is a technique designed to enhance the precision of radiation therapy, and it can be used to treat various types of cancer.
7- Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS): It utilizes multiple precisely focused radiation beams to treat tumors in the brain. Unlike traditional surgery, this method does not involve incisions. Instead, SRS uses three-dimensional imaging to direct high doses of radiation to the targeted area while minimizing the impact on surrounding healthy tissues. The number of sessions ranges from one to three to five sessions, depending on the tumor's size and proximity to sensitive organs.
8- Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT): It uses stereotactic radiosurgery to treat tumors in areas outside the brain, involving multiple sessions ranging from one to three to five. SBRT employs three-dimensional or four-dimensional imaging and precisely focused radiation beams to deliver high doses of radiation to the targeted area, causing minimal damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
9- Electron Radiation Therapy: It is a type of external radiation therapy that treats tumors by directing electrons directly at them. It is often used to treat skin cancer.
10- Hyper Arc: This technique is used for brain tumors, especially when there are multiple tumor sites in the brain. It helps avoid high radiation exposure to healthy brain tissues that might occur with other techniques. Hyper Arc delivers the full dose to scattered tumors while preserving surrounding healthy tissues, using highly advanced algorithms in the field.